
High reliability is one indicator that a measurement is valid. If research has high validity, that means it produces results that correspond to real properties, characteristics, and variations in the physical or social world. Validity refers to how accurately a method measures what it is intended to measure. This indicates that the questionnaire has low reliability as a measure of the condition. Several different doctors use the same questionnaire with the same patient but give different diagnoses. A doctor uses a symptom questionnaire to diagnose a patient with a long-term medical condition. The thermometer displays the same temperature every time, so the results are reliable.

You measure the temperature of a liquid sample several times under identical conditions. Reliability refers to how consistently a method measures something. If the same result can be consistently achieved by using the same methods under the same circumstances, the measurement is considered reliable. However, if a measurement is valid, it is usually also reliable. A measurement can be reliable without being valid. Reliability and validity are closely related, but they mean different things.
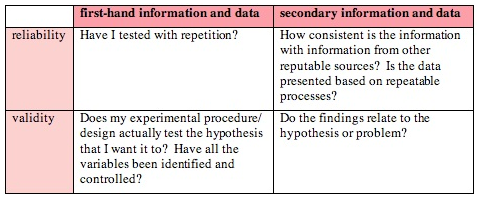

Reliability and validity are concepts used to evaluate the quality of research. Start referencing Reliability vs Validity in Research | Differences, Types & Examples Generate accurate Harvard, APA, and MLA references for free with Scribbr's Referencing Generator.

Probability vs non-probability sampling.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
